| |
“Man told me,” He said, “that these here elevators was Mayan architecture. I never knew that till today. An I says to him, ‘What’s that make me– mayonnaise?’ Yes, yes! And while he was thinking that over, I hit him with a question that straightened him up and made him think twice as hard! Yes, yes!”
“Could we please go down, Mr. Knowles?” begged Miss Faust.
“I said to him,” said Knowles, ” ‘This here’s a research laboratory. Re-search means look again, don’t it? Means they’re looking for something they found once and it got away somehow, and now they got to re-search for it? How come they got to build a building like this, with mayonnaise elevators and all, and fill it with all these crazy people? What is it they’re trying to find again? Who lost what?’ Yes, yes!”
“That’s very interesting,” sighed Miss Faust. “Now, could we go down?”
Kurt Vonnegut, “Cat’s Cradle”
|
The Russian Tea Room, once a popular restaurant created by ballerinas and danseurs (aka male ballerinas) of the Russian Imperial Ballet for themselves and their friends. Later it became an expensive restaurant for the Manhattan high society. In 1996 the new owners closed it down for 4 year and $36 million renovations. In 2002 the restaurant closed, and the owners were bankrupt. In the aftermath, one of the chefs, M.D. Rahman, can be found on 6th avenue and 45th street selling some of the tastiest street food in Manhattan. I bet he’s making more than he did back at the Russian Tea Room now with his little cart.
In the parlance of the Internet this is known as a “redesign” or a “relaunch.” If you are making a living out of web development, like I do, chances are that you participated in a vicious cycle of web site redesigns. They usually happen like this: managers decide to do it and get funding, a lot of meetings follow, specifications are written (or not), arbitrary deadlines are set, designers create graphical mock-ups, then coders swarm and engage in what’s referred to as “death-march.” Managers change their minds about the look and feel a few times during the death-march for an extra morale boost. Finally, a redesigned website launches. Managers start planning the next redesign right away.
In the olden times the CEO’s nephew often got the web design job. Well, these days the nephew grew up, he has a consulting agency. “This is old and busted, let me redesign this mess and you’ll get new hotness” – he says. Pointy-haired bosses everywhere nod and say – “yes, yes, new hotness”, and the cycle keeps on going, redesign after a redesign.
There are a few different types of redesigns. Firs of all, there’s changing the look. In the simplest and best form, this is a very quick deal, especially if the site is properly architected for quick changes. It’s like taking your plain vanilla cellphone, buying a snazzy faceplate, one click – instant new hotness. I have nothing against this sort of redesigns.
The only thing you have to look out for here is what I call the “Felicity effect.” A television show Felicity had a famous redesign failure – the actress Keri Russell cut her trademark long hair. One might argue that she is hot no matter what, but the show suffered a huge drop in ratings. You have to keep in mind that a new look rarely attracts new customers, but often upsets the old ones. For instance, I like Keri’s new look, but I would not start watching that show.

The second type of a redesign involves changing the underlying technology of the site. One might change the content management engine, database engine, rewrite the site in a different language, make it run on a different web server, different operating system, etc. These usually turn out to be the most disastrous and costly of redesigns.
Joel Spolsky wrote about “… the single worst strategic mistake that any software company can make: … rewrit[ing] the code from scratch.” In the web publishing world these kinds of rewrites cause a lot of grief and devastation. A huge technology change always requires a lot of debugging and fixing afterwards, and as soon as most of the bugs are fixed, a new redesign comes around, because, see, ASP.NET 2.0 C# is “old and busted” and Vista Cruiser Mega Platform D## is “new hotness.”
I am not talking here about replacing a technology simply because it does not work or is dangerous. But redesigns are rarely aimed at fixing things – they are done in search of hot technologies and hot looks. By the way, amongst pointy-haired web execs fixing things is less glamorous than perusing new technologies, and that is less glamorous than changing the looks.
A building superintendent I know was in a middle of a huge project – repairing three old and unsafe elevators as well as fixing the crumbling facade of the building. Although the repairs were crucial, they did not earn him the love of the tenants that the old superintendent enjoyed. The old super, instead of fixing broken things, engaged in an almost constant painting projects, changing the color of the paint every time just a little bit. And when he wasn’t repainting, he would leave out the paint bucket and a brush on some rugs in the lobby.
The web execs often go for the best of both worlds – equivalent to changing the foundation of the building (and not the old one was sagging), as well as painting it a new color at the same time. The full Monty web redesign is what the pointy-haired want.
Let’s take a look at the sense that such redesigns make from a capitalist point of view in an area that I know well — web publishing. Web publishing businesses work just like any other. You take some money (aka capital), you spend that money to produce something and you hope that that something makes you even more money one way or another. In economics this is known as Marx’s general formula for capital: Money-Commodity-Money.
Another thing that I faintly remember from my economics class is a rather disturbing concept called “opportunity cost“. See, when you invest money in something you instantly incur this cost. Why? because you can’t invest your money twice, and there always seems to be something you could have invested in that would give you a better return. Let’s say it’s 1995 and you are an editor in, oh, Random House or HarperCollins. You have a budget to publish some children’s books and there’s a pile of proposals on your table. You pick a few. They make money, win awards, etc. Yet, the opportunity cost on every one of those books is about a kajillion dollars, as in that pile there was a certain book by a woman named Joanne Rowling.
In theory, any web executive’s first objective should be to make, and not lose money. Also they should look to minimize the opportunity cost whenever possible. This is of course not the case for many of them. They are thinking: hey I have this fat budget – I can do a big redesign, or …. hmm, what else can I do with that money so it will make me more money?
So how would one go about increasing profits? In the web publishing today content is once again king because of the maturing web advertising, vast improvements in hosting costs and google-inspired web indexing and searching. This was not the case in the earlier days of the web, but now you can directly convert “eyeballs” into profits. The process is rather simple: you create web pages, users visit them, you show users ads (for which you are paid). The relationship is linear – more users = more ad impressions = more money.
So, first of all, you might produce more pages. With search engines like Google, even pages that are hidden in archives of your website will still produce pageviews. The more pages you add, the more revenue you’ll get. In fact, pages with useful information, once placed online become something very dear to a capitalist’s heart – an income generating asset, the very thing that the author of Rich Dad, Poor Dad is so excited about. They are like the geese that lay golden eggs.
The cost of producing more pages comes from three sources: the cost of content – you need to pay someone to write, take pictures, etc; the cost of placing it online – “web producers”, the people who write html, create hyperlinks and optimize images draw a salary; and the cost of hosting/bandwidth – if you are hosting huge videos you costs might be more than what you can get from advertising, but if it’s just text and pictures you are golden. As you surely don’t expect the Spanish Inquisition, there’s the fourth cost: the opportunity cost of showing this content for free, instead of asking for subscription money. The main thing to remember, once the content/feature is created, the costs to keep it online and generating money is trivial.
Besides producing more content, there are other ways of making more money. One might improve the relevance of ads on your pages. If you have a third party ad system, you are pretty much can’t do that. But if you have your own, you might create mechanisms for serving super-relevant ads. Sometimes you might add e-commerce capability to your content website. For instance, if you have a gadget review site, injecting opportunities to easily and cheaply buy the gadgets that you are writing about will likely bring in more more money than machine generated dumb ads.
One might create content that is more valuable to advertisers. For instance, keywords such as “mesothelioma lawyers”, “what is mesothelioma” and “peritoneal mesothelioma” generate ridiculous costs per click on Google’s AdSense. If creating content about “form of cancer that is almost always caused by previous exposure to asbestos” that is so popular with lawyers is not your piece of cake, you can create content about loans, mortgages, registering domain names, etc.
Then we enter the murky waters of web marketing, and especially “SEO” – search engine optimization. In short, if you get other websites to link to your pages, you will get more vistits, partially from those links, and even more importantly, because search engines will place your pages higher in their results. The hard, but honest way to do this is to produce unique, interesting and timely content. No body’s interested in that. Encouraging the readers to link by providing urls that never change and even “link to us” buttons is not in vogue: most web execs prefer non-linkable flash pages. Another way is to pay for links – in the best case for straight up advertising, in the worst case – to unscrupulous “link farm” owners that sell PageRank. Then comes the deep SEO voodoo – changing the file names, adding meta tags, creating your own link farms and hidden keyword pages. At the worst, there’s straight up link and comment spamming. Unethical methods of promoting your business work: Vardan Kushnir who spammed the entire world to promote his “Center for American English” had enough money for booze and hookers, but not many people shed a tear for him when he was brutally murdered (maybe even for spamming). In corporate world the equivalent is the PageRank ban from Google.
So, you could spend your money on all of these things that I described, and hopefully make more money. On the other hand, redesigning a website from top to bottom to make it “look good” or “more usable” will not bring in more “eyeballs”. A redesign of a large site takes several months for the entire web staff. The possible positive aspects of the redesign are these:
1) Faster loading pages
2) Easier to read text
3) More straightforward navigation
4) Cleaner look
6) Bug fixes
7) Switching from a more expensive software and hardware to cheaper
Existing users will probably like you better, but will new ones all of a sudden descend onto the redesigned site? Not likely. In fact, some think that the ugliness of MySpace design is an asset rather than a drawback. People want something from websites. Be it news, funny links, videos, naked pictures, savings coupons or product reviews, design does not matter too much to them. If they can click it, read it and (for the valuable geeks with blogs and websites) link to it – users are generally satisfied.
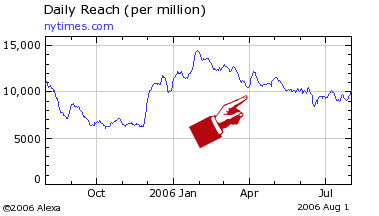
Here’s an example of a well executed major redesign of a high profile website, the New York Times. NYT always had a well designed website, and the new one is pretty nice too. But is there a lot of new traffic? Here’s an Alexa graph.
At the worst redesigns bring:
1) Broken links (sometimes every single url changes and all links from outside break)
2) Heavier graphics, proliferation of Macromedia Flash
3) Slower loading pages
4) Loss of features and content
5) New bugs
6) New software and licensing costs, more expensive servers
Often this is all that they bring. Broken links hurt the search engine positioning. New software costs money. It takes a long while to work out the bugs.
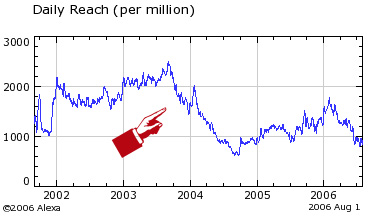
Here’s an Alexa graph of another major redesign on a website, which name I’d like to omit. Just as the traffic recovered after a big redesign in 2000, a new one hit in 2003. It seems to be recovering again.
The thing is, many businesses are very robust and the disastrous effects of web redesigns do not kill them. Pointy-haired bosses make their buddies rich, while getting kudos for the redesigns. Everyone stays busy, and software companies get to sell a lot of server software.